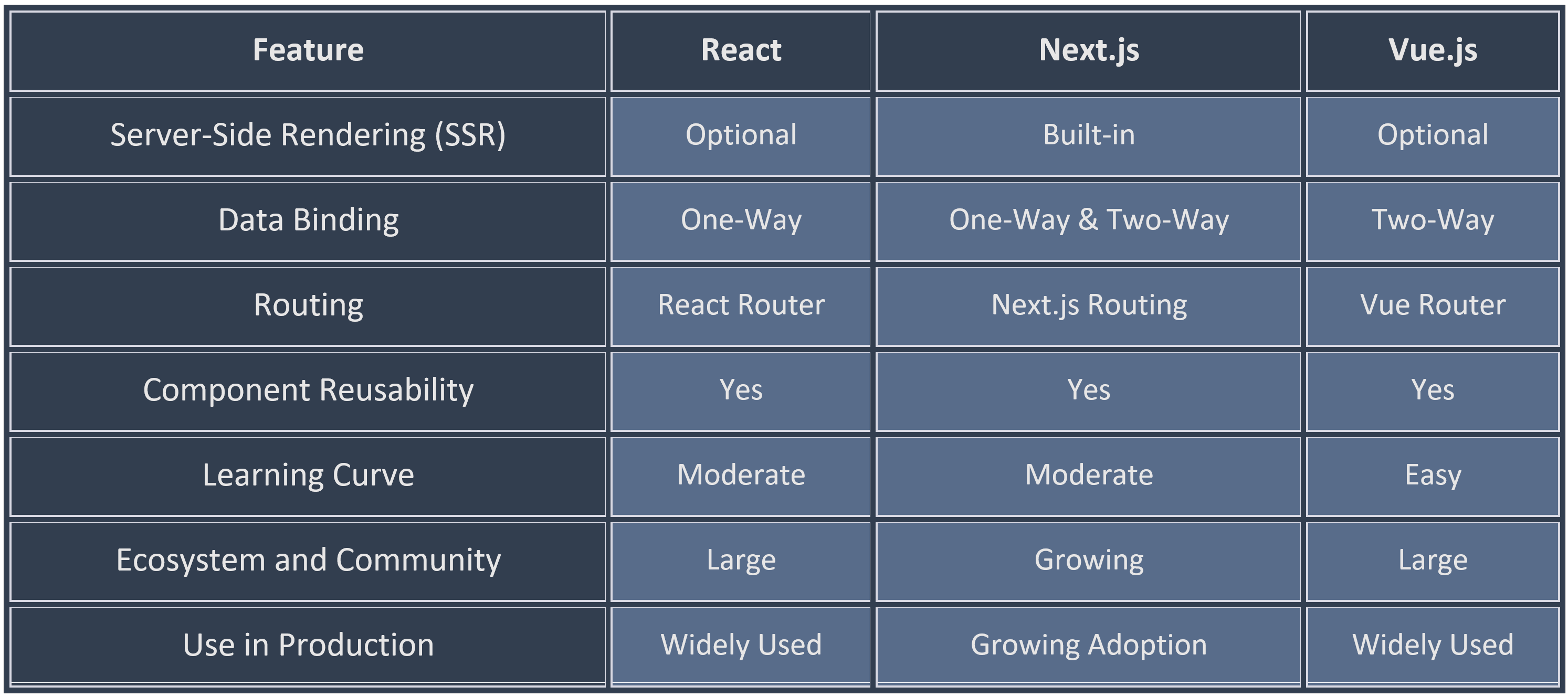
Front-end development has witnessed a transformative shift in recent years, with the emergence of powerful JavaScript frameworks that simplify the creation of interactive and dynamic user interfaces. Among the myriad of options available, React, Next.js, and Vue.js stand out as leading choices for building modern web applications. In this extensive and in-depth blog, we will explore the key features, benefits, and use cases of each framework, empowering you to make an informed decision on which one best suits your development needs and project requirements.
1. React: Power and Flexibility
React, developed and maintained by Facebook, has gained immense popularity for its component-based architecture and virtual DOM rendering. Its declarative approach simplifies the process of building reusable UI components, making it a favorite among developers worldwide.
Key Features:
- Virtual DOM: One of the most significant advantages of React is its efficient use of a virtual DOM, which allows it to update only the necessary parts of the actual DOM, significantly improving performance and rendering speed. This feature ensures smoother user experiences, even in applications with complex and frequent updates.
- Component Reusability: React’s component-based architecture encourages modular development, enabling developers to create reusable and maintainable UI components. This not only streamlines development but also enhances code organization and readability, making it easier to collaborate on larger projects with diverse development teams.
- Large Community and Ecosystem: React boasts a vast and active community of developers who contribute to a thriving ecosystem of libraries, tools, and resources. This wealth of third-party components and extensions enhances development efficiency and enables developers to tap into innovative solutions without reinventing the wheel.
- React Native: Another significant advantage of React is its seamless extension to mobile app development through React Native. By sharing code between web and mobile applications, React Native facilitates cross-platform development, streamlining the process of creating consistent user experiences across different devices.
Best Use Cases:
- Complex Single-Page Applications (SPAs): React’s virtual DOM and efficient rendering make it particularly well-suited for building large-scale SPAs with interactive and data-intensive user interfaces. Popular web applications like Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb leverage React for its ability to handle complex data flows and ensure seamless user experiences.
- Large-scale applications requiring high performance and efficient updates: React’s focus on performance and reactivity makes it an excellent choice for applications that demand real-time updates, such as live streaming platforms, collaborative tools, and financial dashboards.
- Projects that may require future scalability or integration with React Native for cross-platform development: Choosing React is strategic for projects with growth potential, as its scalability and compatibility with React Native future-proof the application for expansion into the mobile realm.
Example: Facebook’s News Feed: The dynamic and interactive nature of Facebook’s News Feed, with its continuous updates and seamless content rendering, is made possible by React’s virtual DOM and reactivity features.
Best Practice: Collect and Analyze User Data: To maximize the benefits of React’s performance optimizations, implement data collection and analysis tools to gather user data and behavior. Use this data to create user profiles and deliver personalized content and recommendations, enhancing user engagement.
2. Next.js: The Full-Featured React Framework
Next.js, built on top of React, adds server-side rendering and other powerful features to simplify the development of server-rendered React applications. It is known for its opinionated approach, providing a structured setup for creating production-ready applications while offering a delightful developer experience.
Key Features:
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): One of the most significant advantages of Next.js is its built-in support for server-side rendering, allowing developers to render pages on the server and deliver fully rendered HTML to the client. This feature enhances search engine optimization (SEO) by making content readily indexable by search engines, leading to better search rankings and improved discoverability.
- File-Based Routing: Next.js organizes pages based on the file system, making navigation intuitive and straightforward. Developers can create new pages by merely adding new files to the designated pages directory, streamlining the development process and reducing the need for complex routing configuration.
- Automatic Code Splitting: Next.js automatically splits code into smaller chunks, optimizing application performance by loading only the required components for each page. This feature results in faster initial loading times, as only essential code is sent to the client on first request.
- API Routes: Next.js provides built-in support for creating serverless functions and APIs within the same application. This integration enables developers to develop APIs directly within their Next.js application, simplifying the process of building full-stack applications.
Best Use Cases:
- Content-driven websites or blogs requiring SEO benefits from server-side rendering: Next.js is an excellent choice for content-focused applications, such as blogs, marketing websites, and e-commerce platforms, where SEO is crucial for driving organic traffic and visibility in search engines.
- E-commerce platforms with dynamic content and serverless backend integration: Next.js’s support for serverless APIs and automatic code splitting makes it a strong contender for e-commerce applications that require seamless integration with serverless backend services and provide a smooth and immersive user experience.
- Projects where fast initial loading and performance optimization are critical: Next.js’s automatic code splitting and server-side rendering capabilities make it ideal for projects where optimizing initial loading times and performance are top priorities, particularly in competitive markets where user retention is heavily influenced by website speed.
Example: Vercel’s Marketing Website: Vercel, the company behind Next.js, uses its own framework to power its marketing website, taking advantage of Next.js’s SEO benefits and effortless integration with serverless APIs.
Best Practice: Implement Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): To maximize the benefits of Next.js’s automatic code splitting and server-side rendering, combine Next.js with CI/CD practices. This integration ensures a faster and more reliable release process, promoting seamless updates and enhancing user experience.
3. Vue.js: Simplicity and Versatility
Vue.js has gained popularity for its simplicity and ease of integration with existing projects. Developed with a focus on simplicity, Vue.js provides an elegant and intuitive approach to building user interfaces, making it a favorite among developers seeking a framework that is easy to learn and use.
Key Features:
- Two-Way Data Binding: One of Vue.js’s notable features is its support for two-way data binding, which simplifies data manipulation and keeps the view in sync with the model. This enables developers to create more interactive and dynamic user interfaces without the need for complex state management.
- Component-Based Architecture: Vue.js shares the same component-based architecture as React, allowing developers to build reusable and modular components. The simplicity of Vue.js’s syntax and structure makes it easy for both experienced and novice developers to work collaboratively on projects.
- Vue Router: Vue.js provides a flexible and powerful routing solution through Vue Router. This feature simplifies the process of managing navigation within single-page applications, enhancing the user experience by providing smooth and seamless transitions between views.
- Vuex: For applications with complex state management needs, Vue.js offers Vuex, a state management library that provides a centralized store for managing application-level data and state. Vuex enables developers to organize and manage application data efficiently, ensuring consistency and reliability across components.
Best Use Cases:
- Small to medium-sized projects where simplicity and fast development are essential: Vue.js’s simplicity and gentle learning curve make it an excellent choice for smaller projects, prototypes, and applications that require rapid development and deployment.
- Applications requiring smooth integration with existing projects or other frameworks: Vue.js’s adaptability and ability to coexist with other frameworks, libraries, or legacy codebases make it ideal for projects seeking to incrementally introduce modern front-end features without disrupting the existing architecture.
- Projects with teams that have diverse levels of front-end development expertise: Vue.js’s approachable syntax and well-defined conventions facilitate collaboration among developers with varying levels of experience, making it an inclusive choice for projects with diverse development teams.
Example: Alibaba’s Double 11 Shopping Festival: Alibaba, one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, utilized Vue.js for its live sales event, Double 11. Vue.js’s simplicity and ease of integration allowed Alibaba to rapidly build and deploy features for a seamless and engaging shopping experience.
Best Practice: Leverage Vue CLI for Project Setup: Vue CLI, a powerful command-line tool, streamlines the process of setting up Vue.js projects by providing a variety of project templates and development features. Utilize Vue CLI to scaffold projects and benefit from its efficient project configuration and build processes.
Choosing the right front-end framework is a crucial decision that significantly impacts your web development project’s success. React, Next.js, and Vue.js all offer unique advantages, catering to different development needs and preferences.
React provides a robust and scalable solution for complex applications, while Next.js simplifies server-side rendering and full-stack development. On the other hand, Vue.js stands out for its simplicity and easy integration with existing projects.
Consider your project’s requirements, team expertise, and long-term scalability when making your choice. React, Next.js, and Vue.js are all valuable tools that can help you build modern, efficient, and engaging web applications. Ultimately, selecting the right framework will empower you to create extraordinary user experiences and elevate your front-end development endeavors, shaping the future of web applications in the era of dynamic and interactive user interfaces.