The Importance of UX/UI in Retaining Users: A Developer’s Perspective
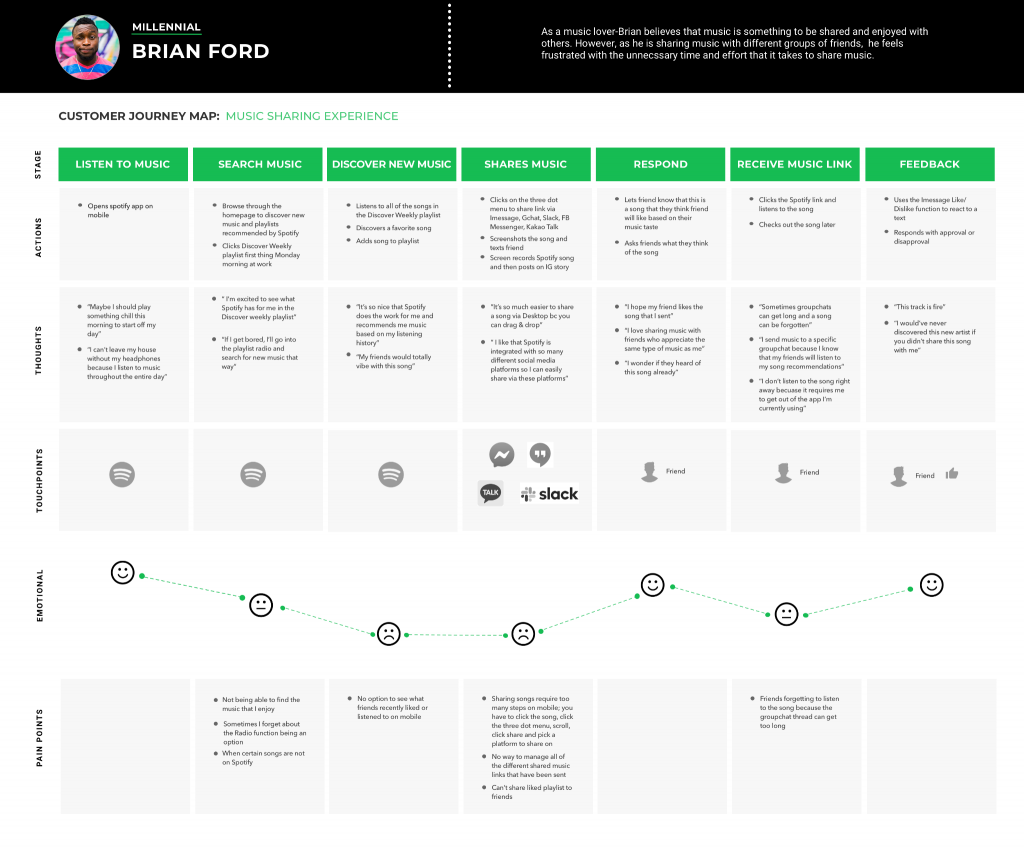
In today’s digital ecosystem, where users have countless options at their fingertips, the battle for user retention has never been more fierce. While robust backend architecture and cutting-edge features are crucial, they’re only part of the equation. The true differentiator that separates successful applications from the ones that fade into obscurity lies in the delicate art and science of User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design. Consider this: the average smartphone user has 80 apps installed but regularly uses only 9 of them. What makes those 9 apps special? The answer consistently points to one factor: exceptional UX/UI design that creates an emotional connection with users while delivering seamless functionality. Imagine stepping into a room and immediately forming an opinion—it’s human nature. In the digital realm, this happens even faster. In just 0.05 seconds, or 50 milliseconds, users decide if they like your app or if they’ll abandon it. This fleeting moment can make or break your app’s success. Understanding the science behind these snap judgments can help developers craft designs that captivate users instantly. Creating an app that “clicks” with users in milliseconds requires attention to design fundamentals: First impressions are more than just aesthetics; they’re the gateway to user retention. By leveraging the science of visual processing, emotional triggers, and effective design, developers can capture attention within milliseconds and set the stage for long-term engagement. When discussing the impact of good UX/UI on user retention, the 15% reduction in churn isn’t just a statistic—it’s a compelling argument for the economic and experiential value of well-designed applications. Let’s delve into the mathematics behind this impact, highlighting how thoughtful UX/UI can directly affect user behavior and, in turn, the bottom line. Poor UX/UI doesn’t merely frustrate users; it costs businesses significant amounts in lost revenue, reduced engagement, and tarnished brand reputation. Here are some critical metrics to consider: Good UX/UI not only prevents churn but actively promotes user retention by creating a smoother, more intuitive user experience. Here’s how developers can turn these numbers in their favor: When you reduce churn by 15%, the long-term financial benefits are substantial. Improved retention leads to: When we talk about a seamless UI, we’re referring to an interface that users can navigate instinctively, without friction or confusion. It’s not just about making things visually appealing—it’s about delivering a holistic, smooth, and natural experience that blends technical brilliance with thoughtful design principles. A seamless UI ensures users stay engaged, feel confident, and enjoy their interaction with the app. Achieving seamlessness requires a robust technical foundation. Here are some key technical considerations: 1. Load Time Optimization 2. Device Responsiveness 3. Accessibility Beyond technical implementation, creating a seamless UI involves psychological and visual design considerations that align with user behaviors. 1. Gestalt Psychology 2. Feedback Mechanisms 3. Transition Design 4. Error Handling In today’s digital landscape, personalization has transitioned from being a luxury to a core expectation. Modern users demand experiences that align with their individual preferences, behaviors, and needs. When done effectively, personalization fosters deeper connections, enhances user satisfaction, and significantly boosts retention rates. Let’s delve into the different levels of personalization, its benefits, and strategies for implementation. 1. Basic Personalization At the foundational level, basic personalization involves simple customizations that make the user feel acknowledged and catered to: 2. Behavioral Personalization This level digs deeper into user behavior to tailor interactions based on observed patterns: 3. Predictive Personalization The most advanced level uses AI and machine learning to anticipate user needs and adapt experiences dynamically: To effectively integrate personalization without overwhelming or alienating users, strategic planning and ethical practices are essential. 1. Data Collection Gathering user data is the cornerstone of personalization. However, it must be done thoughtfully: 2. Segmentation Creating user personas helps in delivering targeted experiences: 3. A/B Testing Continuous improvement is crucial for effective personalization: 4. Privacy Balance Transparency in data usage builds trust and ensures compliance with regulations: Gamification leverages core principles of human psychology to drive user engagement and satisfaction. By integrating game-like elements into applications, platforms, or processes, it taps into intrinsic motivations such as achievement, competition, and recognition. These mechanisms create a sense of accomplishment and enjoyment, transforming ordinary tasks into compelling experiences. When implemented correctly, gamification does more than just entertain—it fosters deeper connections between users and the product. By fulfilling basic psychological needs, it establishes an engagement loop where users feel motivated to return and interact regularly. Gamification thrives on specific design elements that resonate with users’ psychological preferences. Let’s break down these key components: 1. Progress Tracking 2. Achievement Systems 3. Social Components 4. Challenge Systems Gamification isn’t just about flashy visuals or fun features; it’s rooted in deep psychological principles that make it incredibly effective. Here’s how it works: 1. Dopamine Release 2. Social Proof 3. Goal Gradient Effect 4. Loss Aversion In the competitive landscape of app development, data-driven insights can be the deciding factor in allocating resources toward UX/UI improvements. Understanding the measurable effects of poor design not only validates the need for change but also highlights the broader business consequences. Creating exceptional user experiences (UX) and interfaces (UI) involves much more than just creative design—it requires structured planning, technical excellence, and a commitment to continuous improvement. This guide provides an in-depth roadmap for developers aiming to deliver a polished, user-centered app. Let’s break it down step by step. Understanding your users and setting a strong foundation is the first step to creating a seamless UX/UI. 1. User Research Methods To build an app that resonates with your audience, leverage these user research techniques: 2. Design System Development A robust design system ensures consistency and efficiency during development. Focus on these components: The success of any app lies in its performance, stability, and ease of use, achieved through strategic technical efforts. 1. Performance Optimization Optimizing performance ensures a fast and smooth experience: 2. Testing Frameworks Testing is key to delivering a bug-free and delightful experience: An app is never truly finished—continuous monitoring and updates are essential for maintaining relevance and user satisfaction. 1. Monitoring Systems Stay proactive by setting up systems to track app performance and user feedback: 2. Iteration Process Constant refinement ensures your app stays competitive: The investment in exceptional UX/UI design isn’t just about creating beautiful interfaces—it’s about building sustainable business value. When users encounter an app that anticipates their needs, responds to their actions seamlessly, and delivers consistent value, they don’t just use it—they advocate for it. Consider these final statistics: In the end, great UX/UI isn’t just about retention—it’s about creating digital experiences that become an indispensable part of users’ lives. By focusing on these key areas and continuously iterating based on user feedback and behavior, developers can create applications that not only attract users but keep them coming back for more. Remember: In the digital age, user experience isn’t just a feature—it’s the product.The Power of UX/UI in Retaining Users
1. First Impressions: The 0.05-Second Window of Opportunity
The Psychology Behind First Impressions
The human brain processes images 60,000 times faster than text. A visually appealing design creates a strong initial impact, setting the tone for user engagement.
Colors, shapes, and layouts evoke immediate emotions. For example, blue often signals trust and reliability, while bright colors like red and orange can elicit urgency or excitement.
Users subconsciously compare your app’s design to other apps they’ve used. This comparison builds expectations around functionality and usability. A familiar yet fresh design fosters trust.Essential Elements for Powerful First Impressions
Guide users’ eyes effortlessly. Use larger fonts, bold colors, or prominent buttons to highlight key features and encourage action.
Choose colors thoughtfully. For example:
Align the palette with your app’s brand and purpose to create a cohesive emotional appeal.
Fonts should be readable and aligned with your app’s tone. For instance, sans-serif fonts like Helvetica are clean and modern, while serif fonts like Georgia convey sophistication.
Also known as “negative space,” whitespace reduces visual clutter. It helps users focus on essential elements and prevents cognitive overload.
No matter how beautiful your app is, if it doesn’t load quickly, users will leave. Research shows that 40% of users abandon a site that takes more than 3 seconds to load. Optimize load times for a seamless first impression.2. The Mathematical Impact of Good UX/UI on Churn
The Cost of Poor UX/UI
Every user that abandons an app due to poor UX/UI represents wasted marketing dollars. The average cost of acquiring a mobile app user is between $2 and $3 per install. If users drop off within the first few days, these costs multiply without yielding any return on investment.
Poor design can drastically reduce a user’s LTV by up to 75%. For instance, if a user’s projected LTV is $100 but they abandon the app prematurely due to usability issues, the loss is substantial. This reduction impacts the scalability and profitability of the app over time.
Apps with poor UX/UI often suffer from negative reviews. In fact, 88% of users trust online reviews as much as personal recommendations. A single negative review can discourage up to 40% of potential users from even downloading the app.Retention Optimization Strategies
The onboarding experience is the user’s first true interaction with the app. An optimized onboarding flow ensures a seamless start, minimizing friction points such as unnecessary form fields, confusing instructions, or overwhelming feature explanations. Simplifying this process can reduce first-day churn by up to 60%.
Instead of bombarding users with every feature upfront, introduce them gradually. Progressive disclosure enhances engagement by allowing users to explore features organically. This prevents overwhelm and encourages continued usage.
Users frequently abandon apps due to errors, often caused by unclear design. Predictive design strategies, such as autocomplete suggestions or contextual hints, anticipate user actions and guide them effectively. These features reduce error rates and improve user satisfaction.
Even with the best designs, errors are inevitable. What sets great UX apart is the ability to help users recover from them gracefully. Clear, actionable error messages and intuitive recovery paths—like a password reset or undo functionality—can significantly reduce frustration and drop-offs.
Retention doesn’t stop at the launch. Regular analysis of user behavior and drop-off points can identify areas for improvement. Tools like heat maps, A/B testing, and session replays provide valuable insights that guide iterative design enhancements, ensuring the app stays relevant and user-friendly over time.Economic Benefits of Good UX/UI
3. The Architecture of Seamless UI
Technical Components of Seamless UI
Speed is a cornerstone of user satisfaction. Even a minor delay can negatively impact the user experience.
A seamless UI should work uniformly across various screen sizes and devices. Use responsive design frameworks and ensure assets are optimized for both retina displays and lower resolutions.
Technical refinements like keyboard navigability, voice command integration, and assistive text elements are crucial for ensuring your app is inclusive and usable for all audiences.Interaction Design Principles
Design should leverage principles of human perception to ensure that the interface feels natural.
Users expect immediate and meaningful responses to their actions. Feedback is crucial for maintaining confidence and clarity.
Smooth animations and transitions can guide user attention and make the experience feel fluid.
Errors are inevitable, but how they are handled can determine whether users stay or leave. Graceful error handling reassures users and maintains their trust.
4. The Science of Personalization
Levels of Personalization
Implementation Strategies
5. The Psychology of Gamification
Core Gaming Elements
Psychological Triggers
6. Measuring the Impact of Poor UX/UI
Key Metrics to Monitor
This metric reveals the percentage of users who exit the app after interacting with only one screen or page. A high bounce rate often points to issues such as unappealing design, confusing navigation, or technical glitches. Monitoring bounce rates can help pinpoint where users are dropping off and why.
Average session duration indicates how engaging your app is. If users are spending minimal time, it may suggest that the app fails to captivate their attention or fulfill their needs. Longer durations typically signal a better user experience.
This measures the success rate of users completing specific actions within the app, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or uploading a file. A low completion rate might indicate unclear instructions, a cumbersome interface, or unnecessary complexity in workflows.
The frequency of user errors can signal inefficiencies in the design or layout. For instance, users clicking the wrong buttons or misinterpreting instructions are clear signs that the interface isn’t intuitive.
An increase in design-related support tickets often correlates with poor UX/UI. Common complaints about navigation, accessibility, or usability can guide developers toward areas requiring immediate attention.Financial Impact Analysis
Poor UX/UI directly affects your bottom line. Users abandoning a checkout process, canceling subscriptions, or uninstalling the app lead to lost revenue. By analyzing how much potential income is being forfeited due to these factors, businesses can better prioritize design fixes.
When users struggle to navigate or use the app, they often turn to customer support for help. Increased support requests mean additional time, effort, and money spent on resolving issues that could have been avoided with better design.
Comparing your app’s performance metrics with industry standards offers a clear perspective on where your UX/UI stands. If competitors are outperforming you in metrics like task completion rates or session duration, it could indicate that your app’s design needs a revamp.7. Advanced Developer Implementation Guide
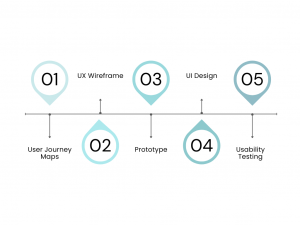
Research and Planning
Technical Implementation
Maintenance and Iteration
Conclusion: The ROI of Excellence in UX/UI